Understand the advantages of deploying and using a Knowledge Graph.
There are many possible definitions of “Knowledge Graphs” but for enterprises and governments, it represents a large network of facts, entities, concepts, and events related to a specific domain, structured to explicitly describe connections among them. It is represented in a machine-readable format based on semantic standards, typically using triples.
A Knowledge Graph model for enterprise integrates and accesses information assets within an organization using data and metadata.
What a Knowledge Graph Encompasses:
A Knowledge Graph serves as a robust framework enabling organizations to:
- Structured Knowledge Representation: Organize and comprehend data in a structured manner, offering integrated, linked, and reusable data while accommodating organizational needs.
- Efficient Information Management: Easily incorporate and manage updated datasets, facilitating meaningful relationships within the data.
- Algorithmic Exploration and Sharing: Analyze graphs for new insights and repurpose data, utilizing formal semantics to handle vast and complex relationships efficiently.
The Benefits of Knowledge Graphs
Contribute to an open, collaborative ecosystem
- Enriching and connecting data fosters an environment of collaboration and openness
Evolving Solutions for Enterprises
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced project initiation costs due to broader adoption and the use of generic triple schema.
- Seamless Integration into existing architectures without system disruptions, enabling decentralization across different linked databases.
- Intuitive Modeling through triplestore format, offering adaptability to constant changes.
Empowering AI Applications
- Knowledge Graphs form the backbone for Semantic AI applications like chatbots, cognitive search using NLP, and self-running systems.
Semantic AI based on EKGs can be used for everything from searching and displaying information, as well as smart semantic AI applications (chatbots, cognitive search using Natural Language Processing —NLP, product advisers, and self-running systems…).
A Knowledge Graph gives AI applications intelligence.
Leveraging your enterprise knowledge graph can offer you more than just extracting and linking data, providing recommendations and insights:
- Facilitate the access, integration, interpretation, and recognition of entities in context, by connecting them to content and data sources.
- Provide a robust framework for content management, personalization, and interoperability of semantic data.
- Enrich semantic search with connections and relationships between data points for better insights.
- Enable users to find better solutions to address growing volumes of structured and semi-structured data.
- Enable users to make better decisions by showing them non-obvious information.
- Help identify trends, anomalies, gaps, etc. in various areas through deductive reasoning.
- Enables the design of data-centric user interfaces.
- Enables the creation of specific tools for the use cases best served by graph technology, such as business intelligence, expert systems, 360-degree views of customers, fraud detection, and investigative intelligence.
RDF & Knowledge Graph
Organisations can foster interoperability and a common language across platforms by moving away from conventional relational databases to enterprise knowledge graphs.
It is challenging to manage organisational knowledge when it is scattered across a wide range of disparate, siloed systems. By using RDF (Resource Description Framework), it is possible to build highly interconnected, interoperable, and flexible information structures.
The image that comes to mind when you hear the word ‘graph’ is probably like this: entities – the nodes – are often represented by circles – and relationships – usually by lines connecting the nodes.
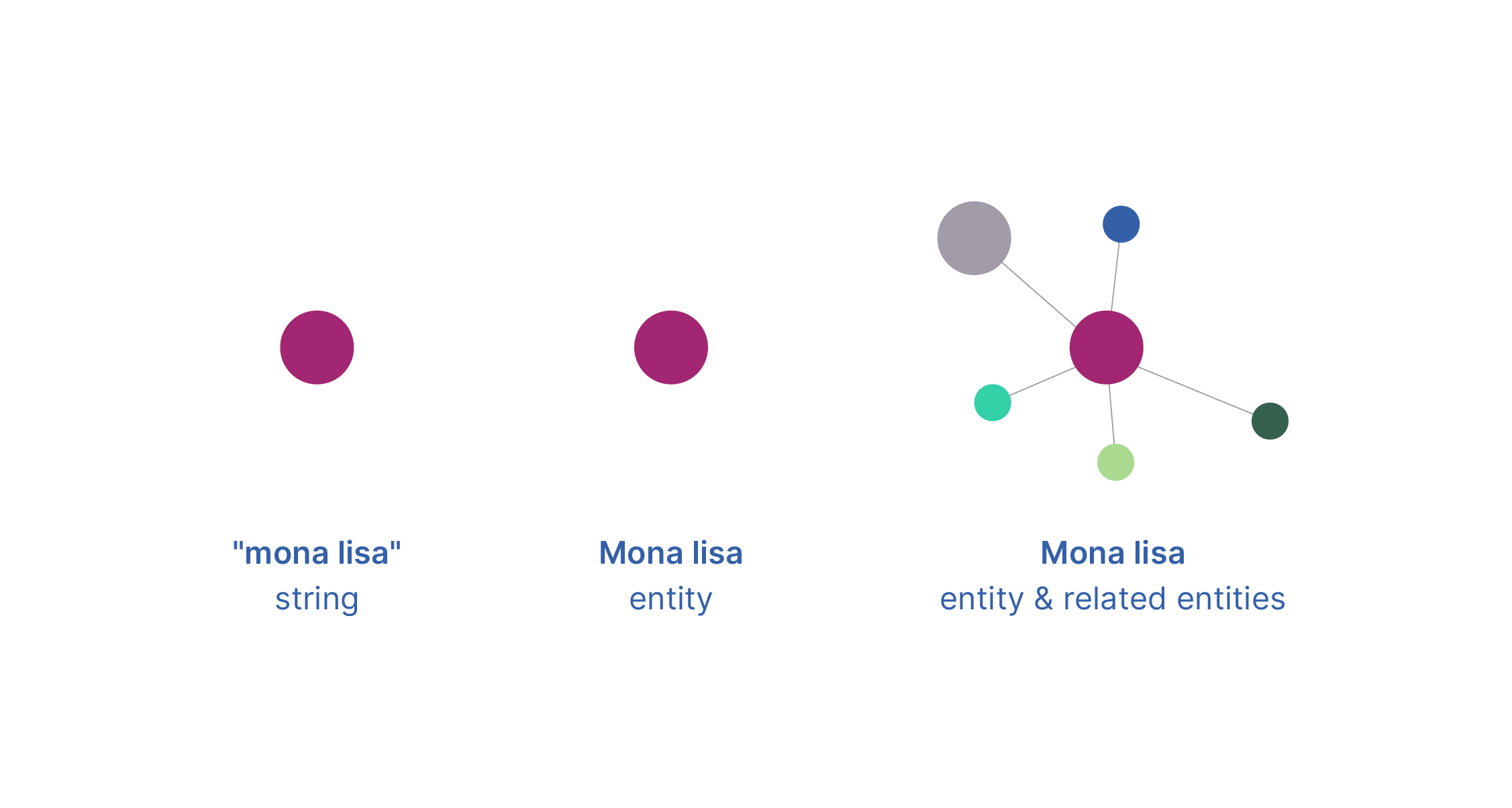
This could be illustrated in a multidimensional network model, which reveals not only facts A and B, but also their relationships.
And this is how the RDF data model works.
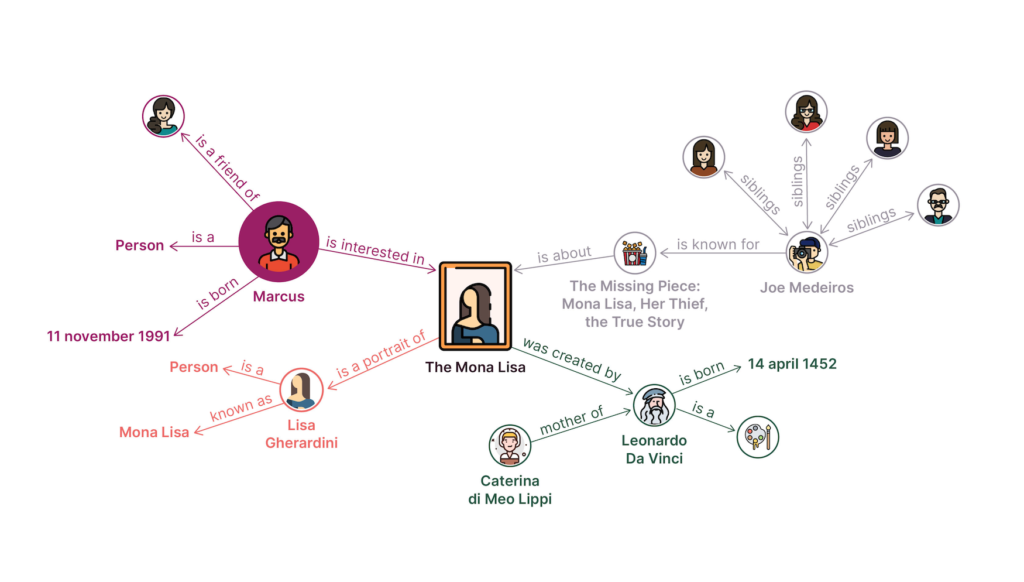
Organisations that want to effectively manage data in order to reduce development and maintenance costs for their systems can no longer rely on traditional approaches if they want to manage data intelligently.
With semantic data models, you can combine your business data with analytics and algorithms through the use of a model that is separate from analytics and algorithms. Semantic data models provide the best framework for integrating, unifying, linking, and reusing your business data.
It offers a multitude of ways to enrich the EKG, with limited administrative burden and proven scalability:
- Enable communication between humans and computers by allowing schemas, ontologies, and data to be interpreted unambiguously (It makes data understandable in business terms rather than cryptic codes understood by only a few experts).
- Facilitate the modelling of sources and other structured metadata (data schema, taxonomies, vocabularies, all sorts of metadata,…).
- Support the management and storage of complex and large datasets containing hundreds of billions of facts.
- Provide open standards (RDF is a W3C standard), implementing unique identifiers to facilitate data integration and publishing.
- Allow information to be easily identified, disambiguated, and interconnected by AI systems.
- Offer more flexibility to data changes than other data models (schema is not redefined every time new data is added).
- Widely implemented, it gives access to large datasets from various free sources (DBpedia, GeoNames, Wikidata, etc.) whose volume is increasing every day.
- Reduce costs by operating more effectively and enabling the automation of some management processes
Elevate Your Data into Knowledge with Cognizone
The extensive advantages of deploying Knowledge Graphs pave the way for transformative possibilities within organizations and governmental entities. From structured knowledge representation to empowering AI applications and offering robust frameworks for data management, the profound value of Knowledge Graphs in reshaping data landscapes is undeniable.
At Cognizone, we recognize the potential of Knowledge Graphs and extend our expertise to further harness their capabilities. Our services are tailored to amplify the advantages highlighted by Knowledge Graph deployment, enabling organizations to extract maximum value from this transformative technology.
- Semantic Technologies and Linked Open Data to extract maximum value from your data
- Knowledge Graph Implementation to gain a comprehensive 360-degree view of your enterprise data.
- Migration to Semantic Data to seamlessly migrate your data to a semantic format.
- Semantic Data modeling to create intuitive semantic models that simplify data comprehension and usage across your organization.
- Semantic Data Publication to publish your data in a semantic format, facilitating easy consumption by all your teams and more.
- Software Development to create with you smart digital solutions prioritizing your business goals and tailored to data needs.
- Consultancy to help you define your data needs for tangible business outcomes, leveraging semantic data and Knowledge Graph solutions.
We believe that each customer faces unique challenges and our services are designed to best address them.
The Enterprise Knowledge Graph implementation does not follow an identical methodology from one enterprise to another. Many parameters must be considered for such a project’s success.
Inspired by our experience in a wide range of contexts, both in terms of the business sector, size and corporate culture, we aim to develop systems that are customised to your business cases and individual needs.
We are known for our flexibility and tailoring and are committed to delivering dedicated experiences that enhance the work of all data stakeholders.
When all parameters are considered, you can build a more manageable and efficient network, with datasets that are easier to integrate, discover, access, link, and integrate.
Some Knowledge graphs in use
FactForge is an RDF graph representing news, people, organizations, and places.
Geonames is a geographical database containing over eleven million placenames
Wordnet is a lexical database containing English nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs
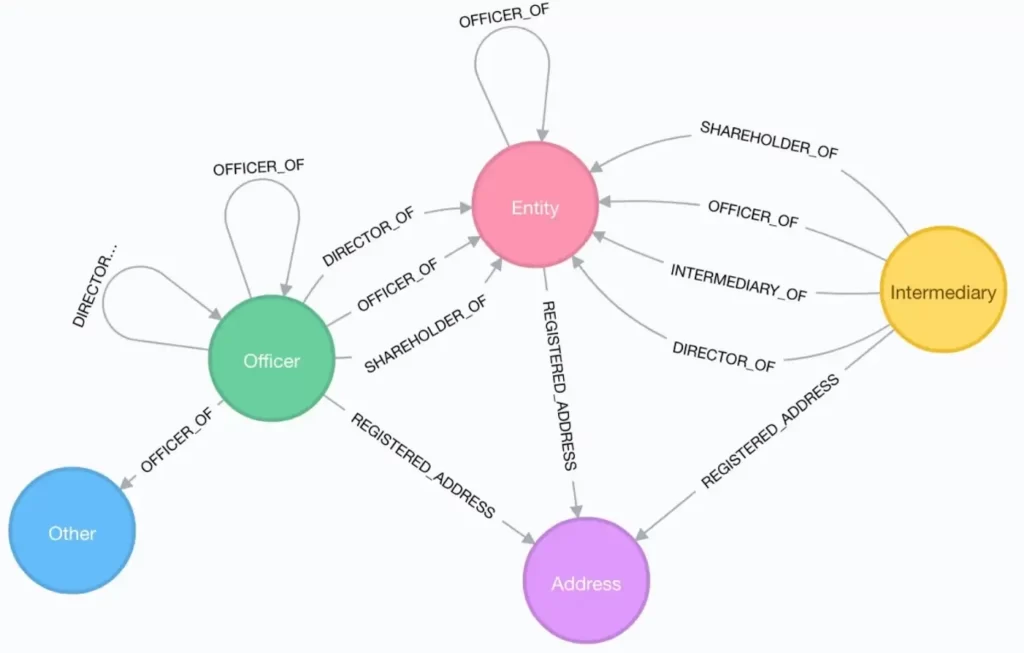
The Panama Papers are an unprecedented leak of 11.5m files from the database of the world’s fourth biggest offshore law firm, Mossack Fonseca.
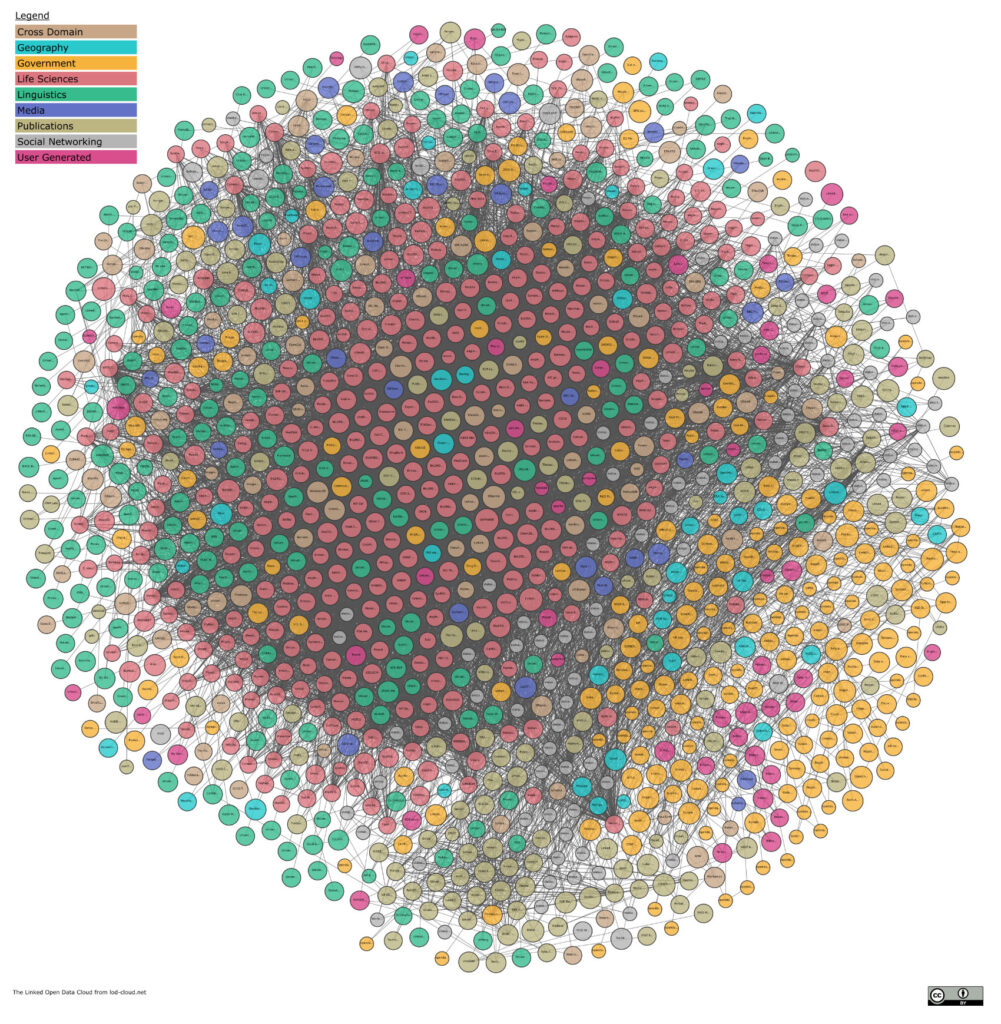
The LOD cloud diagram is a visualization of 1579 datasets with over 16,200 links. Each vertex is a separate dataset structured as a knowledge graph.
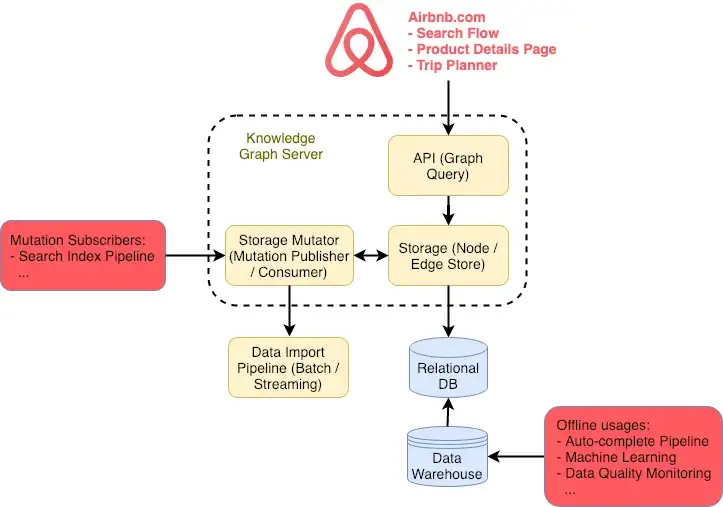
Airbnb knowledge graph is containing a very large database of place, events, experiences, people, travel destination.
Takeaways
- Knowledge management and data integration as Knowledge Graphs are evolving to meet enterprise production requirements, including stability, availability and security.
- A Knowledge Graph represented by RDF and defined by OWL models is highly flexible. It provides the most appropriate framework for data integration, unification, linking and reuse, whilst maintaining the lineage of data sources. When a huge amount of data from disparate sources is processed, it is essential to know where the data comes from to ensure quality and compliance.
- Knowledge graphs are a prerequisite for the creation of specific applications powered by intelligent and semantic AI such as business intelligence, expert systems, 360-degree views of customers, fraud detection and investigative intelligence.
- Knowledge graphs enable communication between humans and computers by allowing schemas, ontologies and data to be interpreted unambiguously. It makes data understandable in business terms rather than cryptic codes understood by only a few experts.
- Knowledge graphs offer you the most robust framework to discover new facts about your data and gain new insights into your organisational knowledge that otherwise would remain unnoticed.